Category: News
-

By Paolo Rega In the high-stakes battle against tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections, scientists are turning to an unlikely ally: viruses that infect bacteria, known as bacteriophages. A groundbreaking study published in Cell by Krista Freeman and colleagues unveils the atomic-level structure and infection dynamics of one such virus—mycobacteriophage Bxb1—offering new hope for precision phage…
-
A groundbreaking study published in Bone Research reveals a novel approach to creating high-quality mitochondria that could revolutionize treatments for osteoarthritis and other metabolic disorders. Researchers from Zhejiang University in China have developed an “organelle-tuning condition” that dramatically increases both the quantity and quality of mitochondria produced from human mesenchymal stem cells. The Mitochondrial Challenge…
-
By Paolo Rega In a groundbreaking advance for genetic engineering and immunotherapy, researchers at the Karolinska Institutet have unveiled a novel optogenetic CRISPR system that enables precise, light-controlled gene editing in T lymphocytes — even inside living organisms. The system, dubbed BLU-VIPR (Blue Light-inducible Universal VPR-Improved Production of RGRs), allows scientists to turn gene editing…
-
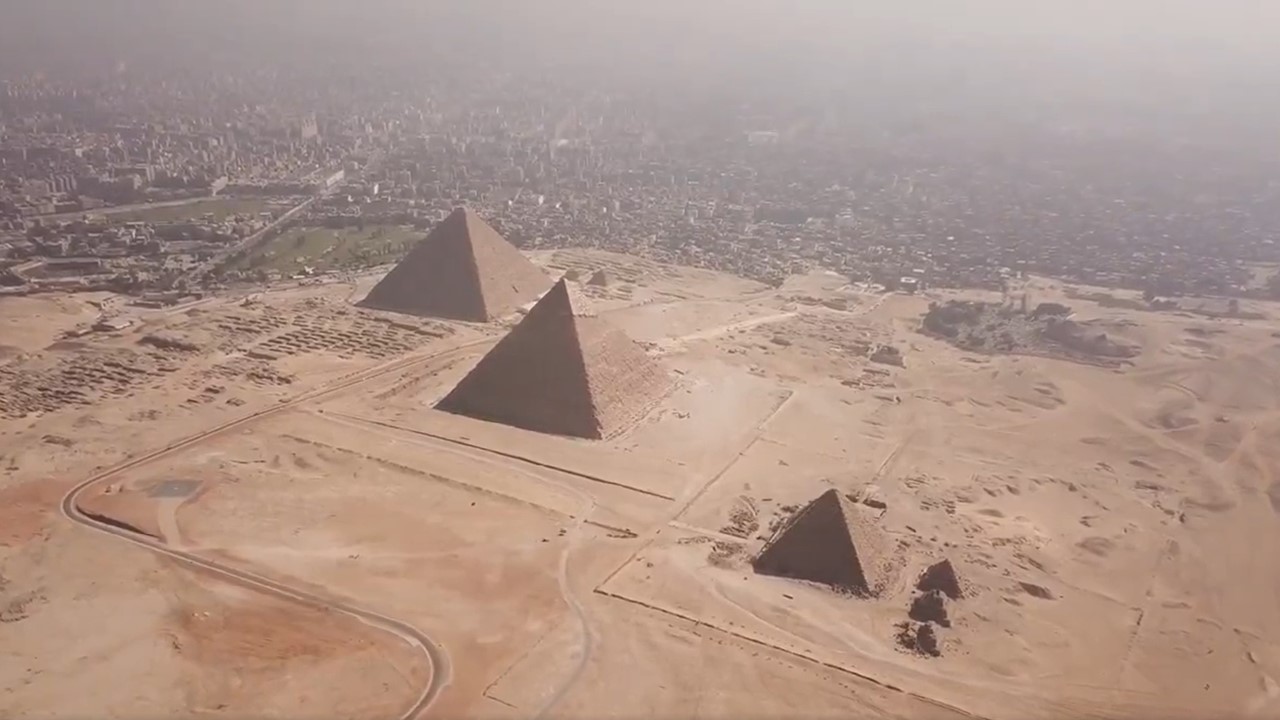

A new frontier in archaeological science has opened high above the sands of Egypt. Using advanced radar imaging from orbit, the team of researchers led by Filippo Biondi and Corrado Malanga has mapped the internal architecture of the Great Pyramid of Giza — one of humanity’s oldest and most studied monuments — with extraordinary detail.…
-
In an era where antibiotic resistance threatens to undermine modern medicine, researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery that could revitalize our ability to treat deadly bacterial infections. A recent study by Wang et al. reveals how tiny cellular messengers can silence the genes that make bacteria resistant to antibiotics, potentially providing a powerful new weapon…
-

The rising threat of antibiotic resistance presents a critical challenge to global healthcare. Conventional antibiotics are becoming less effective, with multidrug-resistant bacteria and fungi endangering millions of lives annually. To address this crisis, researchers of some Chinese universities have turned to artificial intelligence (AI) as a tool for the de novo design of antimicrobial peptides…
-

The human brain is a marvel of evolution, exhibiting unique features such as an increased cortical surface area, prolonged neurogenesis, and advanced synaptic plasticity. Scientists have long sought to unravel the genetic factors behind these developments. One crucial discovery in this domain is the presence of Human Accelerated Regions (HARs)—stretches of DNA that have remained…
-

A groundbreaking study carried out by the researchers of the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) has unveiled a new way to combat cancer by reprogramming fat cells to outcompete tumors for essential nutrients. Researchers have developed a method called adipose manipulation transplantation (AMT), where engineered adipocytes—fat cells—are implanted near tumors to deprive them of…
-

In the battle against infectious diseases, antibiotic resistance remains one of the most pressing global health threats. A recent study published in Nature Communications sheds light on a crucial driver of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacteria: the hypermutation caused by DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency. The research, focusing on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, underscores the role of…
-
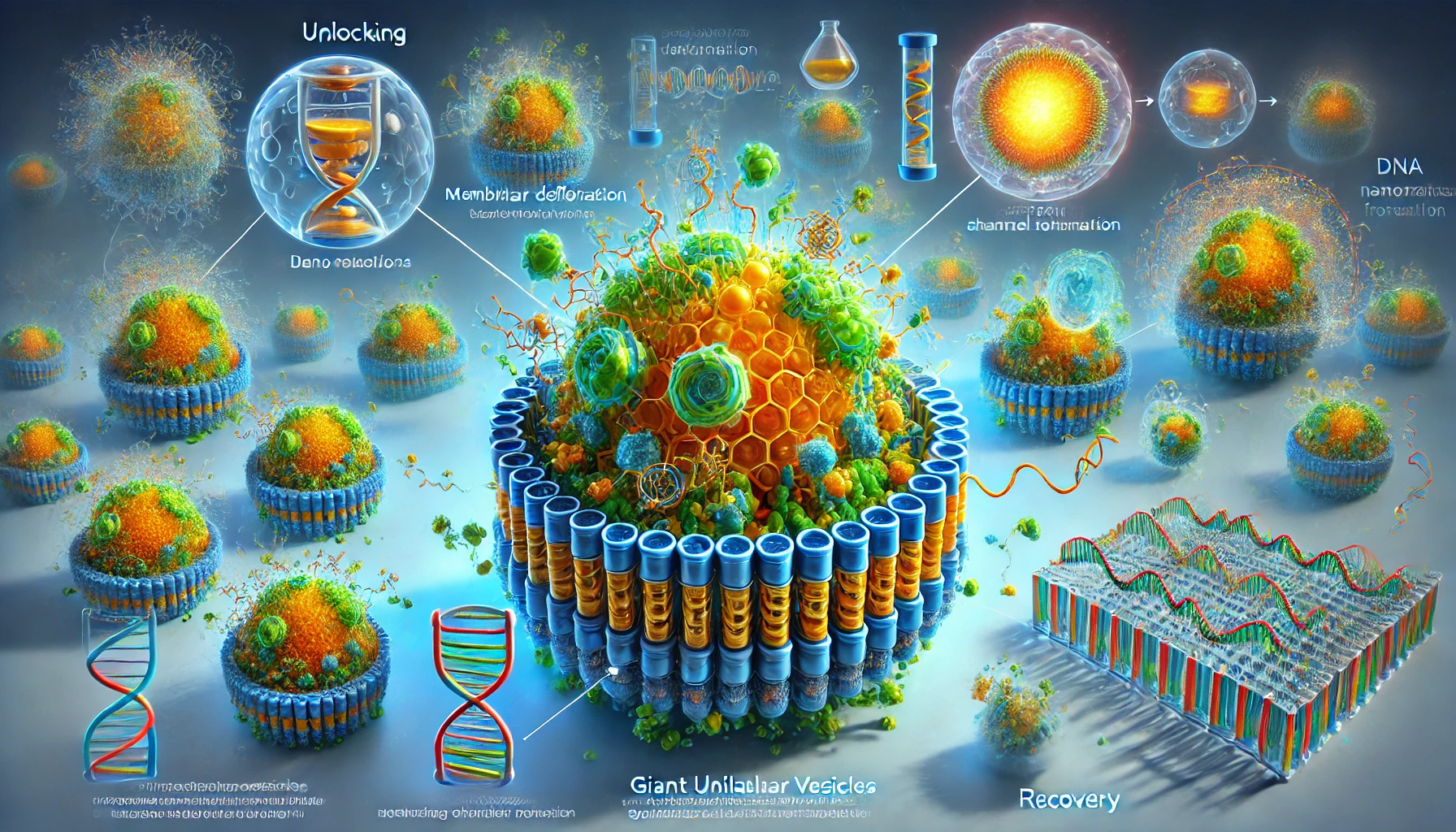
In a breakthrough study published in Nature Materials, scientists at the University of Stuttgart have unveiled an innovative approach to manipulating synthetic cells by leveraging reconfigurable DNA nanorobots. This research bridges the nanoscale and microscale worlds, offering a sophisticated method to reshape cell membranes and create functional synthetic channels, potentially revolutionizing synthetic biology. The Role…
